Unlocking Ethereum's Potential: The Promise of Based Rollups
Based rollups enhance Ethereum by using Layer 1 for sequencing, reducing fragmentation & boosting ETH’s security. Learn how they shape Ethereum’s future!

As Ethereum continues to evolve, the quest for scalability and efficiency remains of prime importance. One of the recent trending topics, based rollups have emerged as a compelling approach to enhance Ethereum's performance and value proposition. This article delves into the intricacies of based rollups, their distinction from other rollups, the role of Ethereum as a sequencer for L2s, and the implications for Ethereum's ecosystem and its native asset, ETH.
How did we get here?
The short story is that as Ethereum became more and more popular with a huge amount of new protocols built upon it and new users using it, the gas fee on Mainnet became too high. Sometimes shockingly expensive, reaching a few hundred US dollars per single transaction. This led to the creation of a rollup-centric roadmap with the goal of off-loading execution to L2s. Successfully the gas became cheaper and the TPS (transactions per second) increased. Sounds good, right? But this itself led to some new complications. More and more Ethereum L2s started popping up. Arbitrum and Optimism were the first that got really big and all seemed moving in a good direction. Then we got dozens of more L2s which led to problems like fragmented liquidity and centralized sequencers. Sequencers are responsible for the ordering and submission of transactions to Ethereum (or other chains). This ordering is crucial because the sequence of transactions affects the state updates and outcomes of decentralized applications (dApps) operating on the rollup.
Users of Ethereum became so scattered across different rollups that the question of is Ether (the asset) dying became more and more common.
Understanding Based Rollups: A New Paradigm in Layer 2 Scaling
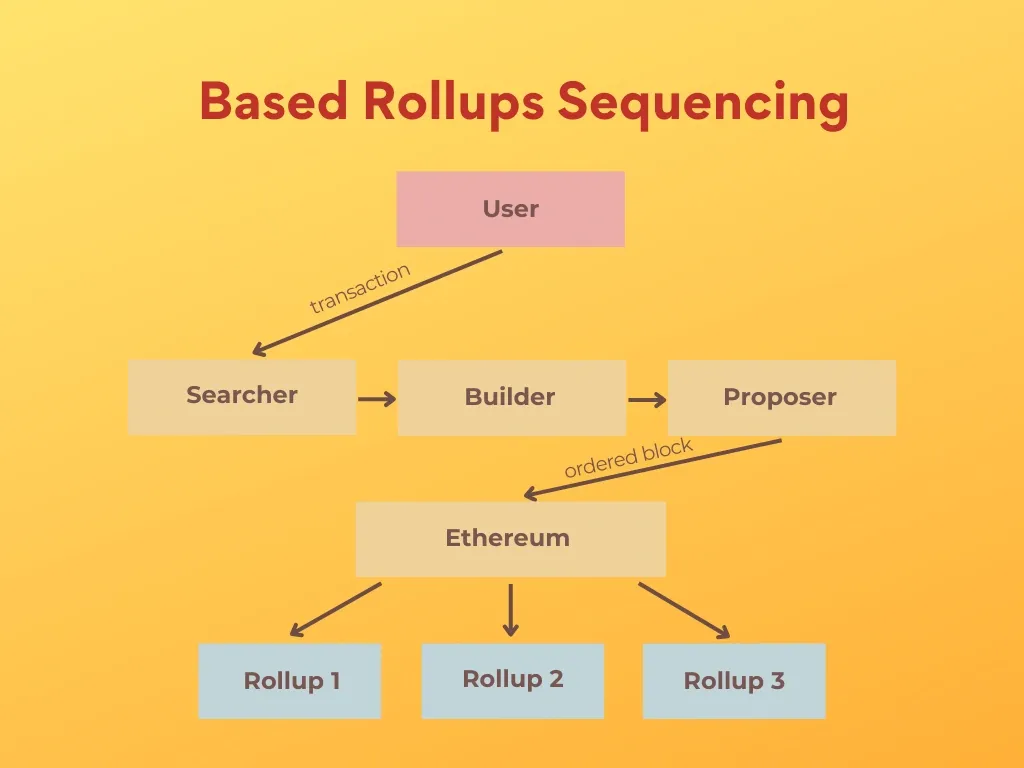
Traditional rollups, using optimistic and zero-knowledge (ZK) tech, have been key in scaling Ethereum by processing transactions off-chain and subsequently submitting compressed data back to the mainnet. Optimistic rollups assume transactions are valid by default, introducing a challenging period for fraud proofs, while ZK rollups use cryptographic proofs to validate transactions before posting them on-chain. Both approaches, however, usually rely on their own sequencers to order transactions, which introduces centralization risks and operational complexities.
In contrast, based rollups delegate the sequencing function to Ethereum's Layer 1. This means that the base layer blockchain, Ethereum in this context, manages the ordering of transactions for the rollup. By leveraging Ethereum's inherent decentralization and security, based rollups aim to simplify the sequencing process, reduce operational overhead, and enhance alignment with the base layer's economic incentives.
Ethereum as the Optimal Sequencer for Layer 2 Rollups
The proposition of utilizing Ethereum Layer 1 as the sequencer for Layer 2 rollups is grounded in several compelling advantages:
Liveness and Reliability
Ethereum has demonstrated consistent uptime (effectively 100%) and resilience over the years. By entrusting transaction sequencing to Layer 1, based rollups inherit these robust uptime guarantees, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted transaction processing.
Decentralization
Traditional rollups often depend on centralized or semi-centralized sequencers, which can become points of failure or censorship. Based rollups, by leveraging Ethereum's decentralized validator network, mitigate these risks, promoting a more censorship-resistant and trustless environment. Furthermore, even if a Rollup uses a decentralized sequencer, if more and more Rollups choose Ethereum as a sequencer this will drastically lower the liquidity and user fragmentation. More on that later.
Economic Alignment
By integrating sequencing into Ethereum's Layer 1, based rollups align their economic incentives with the base layer. This synergy can lead to more sustainable fee structures and value accrual mechanisms that benefit both the rollup and Ethereum's broader ecosystem.
Addressing Ethereum's Fragmentation Through Based Rollups
One of the challenges Ethereum faces is the fragmentation of liquidity and user experience across various Layer 2 solutions. Each rollup often operates as a siloed environment, necessitating bridges and complex mechanisms for interoperability.
Based rollups offer a pathway to mitigate this fragmentation:
Synchronous Composability
By utilizing Ethereum Layer 1 for sequencing, based rollups can achieve synchronous composability. This means that transactions across different rollups can be processed within the same Ethereum block, enabling seamless interactions between decentralized applications (dApps) on different rollups without the need for bridging delays.
Unified Liquidity
With synchronous composability, liquidity is no longer fragmented across multiple Layer 2 solutions. Users and developers can access a unified liquidity pool, enhancing capital efficiency and improving the overall user experience.
Simplified Infrastructure
By standardizing Ethereum Layer 1 for sequencing, the infrastructure becomes more streamlined. Developers can build on a consistent foundation, reducing the complexity associated with deploying and maintaining multiple rollup-specific sequencers.
So Based Rollups sound perfect, right? Almost. Based sequencing operates at L1 block times (12 seconds). One of the reasons why users love L2s is the almost instant transactions. Can this be fixed? Enter preconfs.
What are preconfs?

Commitments from validators to users. About doing something related to the block proposal. If the promise is broken, then the validator can get slashed.
Implications for ETH as an Asset
The integration of based rollups has significant ramifications for ETH, Ethereum's native cryptocurrency:
Increased Demand for ETH
As based rollups utilize Ethereum Layer 1 for sequencing, the demand for block space and consequently, gas fees on Ethereum is expected to rise. This increased usage can lead to higher ETH burn rates under the EIP-1559 fee mechanism, potentially making ETH more scarce over time.
Enhanced Staking Yields
Validators on Ethereum may see increased rewards as they participate in sequencing for based rollups. This could make staking ETH more attractive, leading to higher network security and further incentivizing ETH holders to participate in staking.
Strengthened Economic Security
The alignment of economic incentives between based rollups and Ethereum Layer 1 can bolster the overall economic security of the network. As more value flows through Ethereum, the network becomes more robust against potential attacks, enhancing confidence in ETH as a store of value.
Conclusion
Based rollups represent a promising evolution in Ethereum's scaling strategy. By leveraging Ethereum Layer 1 for transaction sequencing, they offer a pathway to greater decentralization, reduced fragmentation, and enhanced economic alignment within the Ethereum ecosystem. For ETH as an asset, the adoption of based rollups could lead to increased demand, improved staking incentives, and strengthened economic security, all of which contribute to a more robust and valuable Ethereum network.
As the Ethereum community continues to innovate, based rollups stand out as a compelling solution to some of the network's most pressing challenges, paving the way for a more scalable and interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
